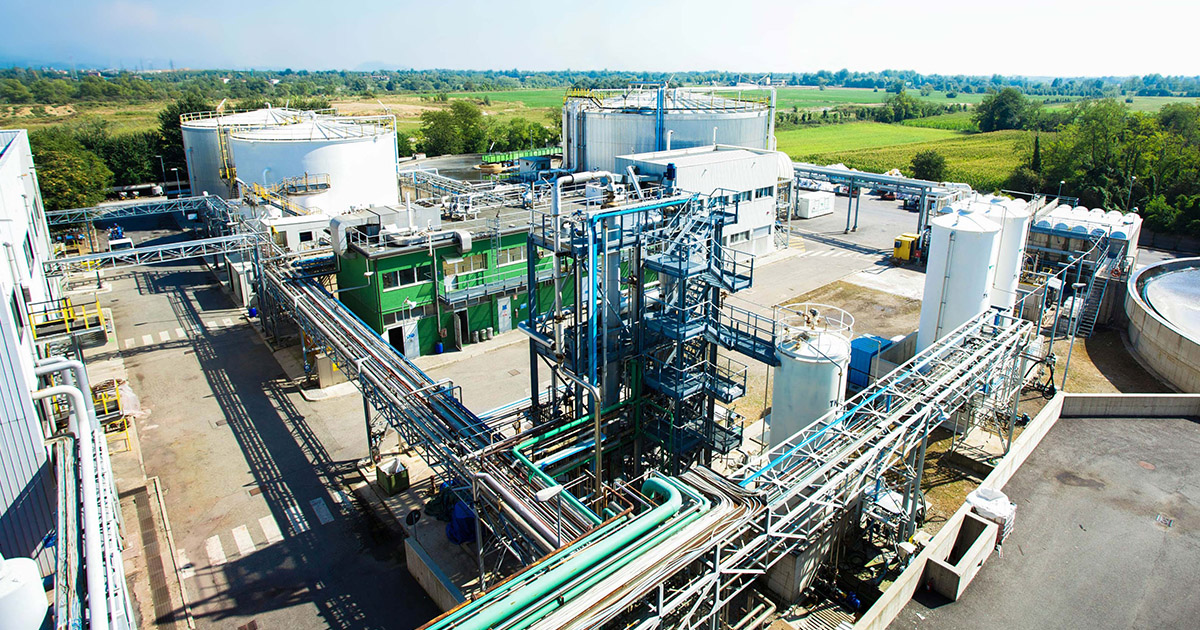
Plants
Wet oxidation – Dual TOP technology
Wet oxidation (WO) is an extremely versatile hydrothermal process that can be used to treat wastewater with high COD content and/or containing refractory compounds hard to degrade, and to reduce sludge mass and the presence of other substances or microorganisms potentially dangerous to people’s health and to the environment.
Our unique patented Dual TOP technology can simultaneously treat wastewater and biological sludge.
WO consists in the oxidation of dissolved and suspended pollutants, including refractory ones, at elevated temperature and pressure using oxygen or air as the oxidizing agent.
The elevated operating pressure maintains water in the liquid phase and improves the oxidation rate by increasing dissolved oxygen concentration. Pollutants are effectively converted to carbon dioxide, water, and intermediate oxidation products (smaller molecules).
The volatile (organic) suspended solids are almost completely removed with a sludge mass reduction of up to 80%-90%. The remaining solid, mainly inorganic, can be easily settled and dewatered: a strong reduction of sludge disposal costs is so pursued.
The liquid stream is detoxified, odour and colour are almost completely removed and its COD content is strongly decreased. The remaining COD is mostly represented by highly biodegradable, low molecular weight compounds that can be treated in standard WWTP.
Catalytic wet oxidation may also be employed to achieve greater destruction operating at lower temperatures and pressure or reduced oxidation time. The aqueous stream is mixed with a catalyst before undergoing the oxidation process.
Overview
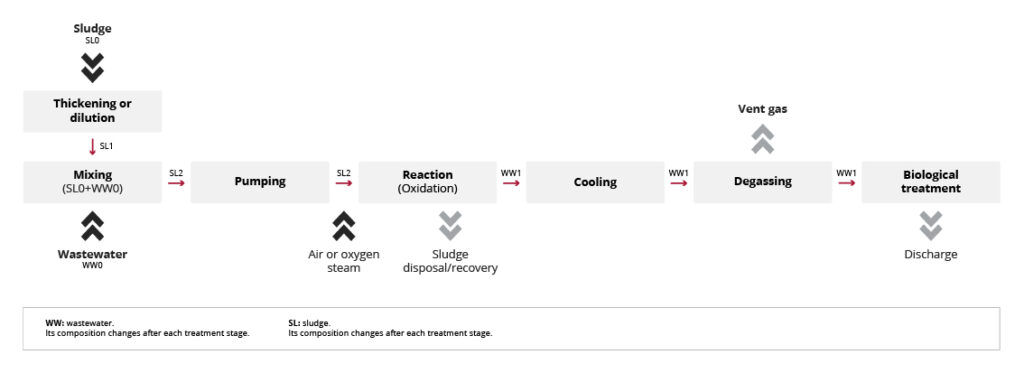
Show more Show lessA WO plant mainly consists of the following sections.
- A slurry, with a proper COD and solid content is prepared mixing thickened sludge and wastewater to be treated. The slurry is then routed to the feeding tank.
- From the feeding tank the sludge stream is sent to the WO plant with pumps, increasing the stream pressure up to the reactor operating pressure.
- In the reactor, the slurry is mixed with the oxidizing agent (air or oxygen) and the high-pressure steam needed to reach the proper operating temperature.
- Heat from the reaction is partially recovered through the steam generated during the depressurization steps, reducing significantly the required energy input.
- Process off-gases from the separator are usually routed to further treatments (e.g., thermal oxidizer, biofilter, biological plant).
- The residual solid present in the final effluent is separated by a static decanter and a centrifuge; the liquid effluent, highly biodegradable, is polished by biological treatment.
Features and rangeability
Show more Show lessWe customise the size of WO plants according to the type of waste to be treated and to the customer’s performance expectations. Plants are typically operated within the following ranges:
- Feed flow rate: 1 m3/h to 20 m3/h
- Treated biological sludge per year: 600 tons to 13.000 tons as dry sludge
The most suitable material is selected depending on the operating conditions.
The main materials usually selected are the following:
- Stainless steel
- High performances alloys
WO plants are supplied as pre-fabricated modules (skid mounted units), thus minimising the installation operations to be performed at the customer’s site.
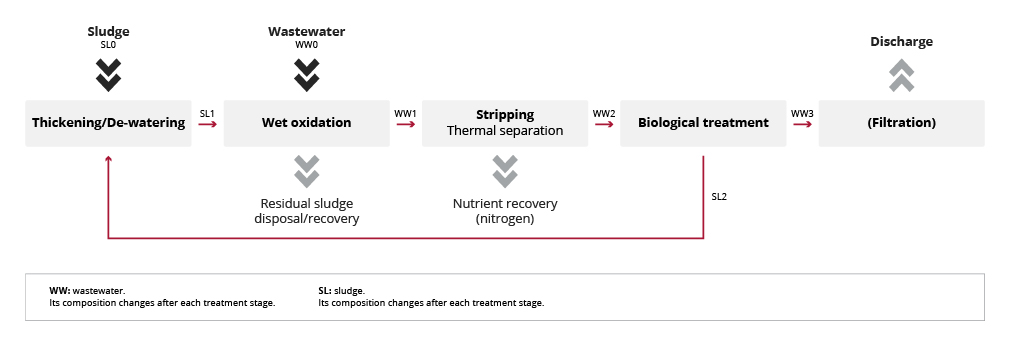
Wet oxidation plants are typically coupled with biological treatment for effluent polishing and can be integrated with stripping to recover nitrogen as a nutrient.
Key benefits
Show more Show less- Relevant savings on sludge disposal costs
- Near complete detoxification of the liquid stream (increased biodegradability)
- Reduced environmental footprint
- Maximum operating flexibility (in feed composition and flowrate)
- Minimum maintenance downtime due to cleaning procedure
- Maximum energy savings
- High automation level
- Reliability
Applications
Show more Show lessDual TOP technology can be used to treat different kinds of biological sludge and wastewater, both municipal and industrial, originating from a wide range of industries, such as:
- Chemical
- Iron and Steel
- Landfill
- Petrochemical
- Pharmaceutical
- Pulp and Paper
- Tanning
- Textile
Multiple goals are achieved in one step:
- Up to 80%-90% reduction of sludge mass
- Up to 96%-98% oxidation of suspended organic (volatile) solids
- Up to 70% COD removal
- Increased sludge settleability and dewaterability
- Removal of harmful and bio-refractory organic pollutants
- Removal of microbes
Depending on the quantity, composition and the customer’s needs, sludge and wastewater can be treated separately using TOP technology.
More about wet oxidation – TOP technology
More about wet oxidation for biological sludge
The broad range of industrial processes generates extensive sludge compositions and each composition requires a customised process and a bespoke plant design.
We provide support to our customers conducting tests as well feasibility studies leveraging our R&D centre and multi-disciplinary teams.
References