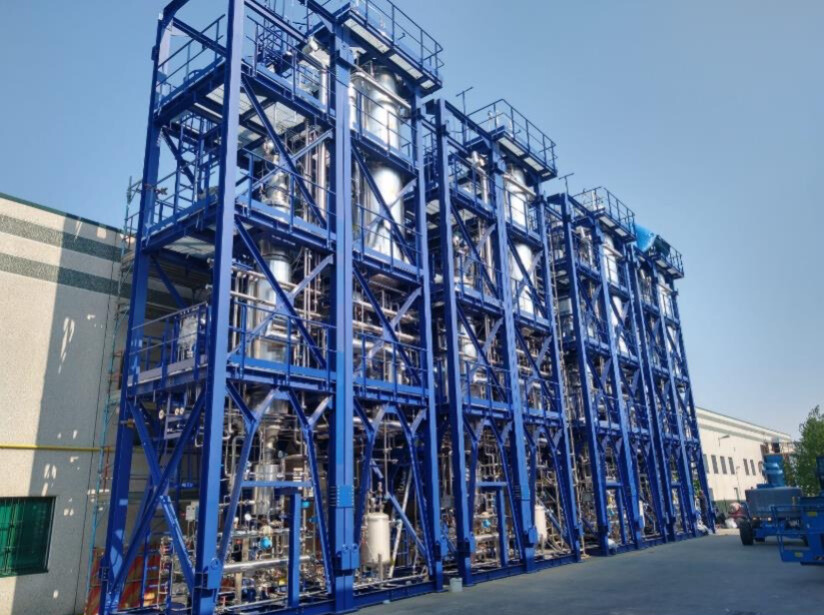
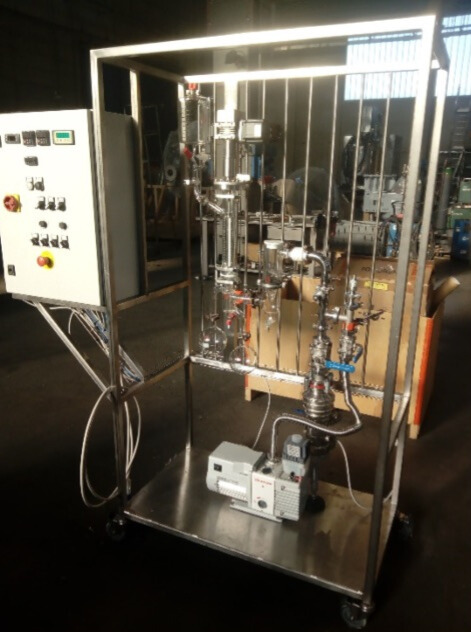
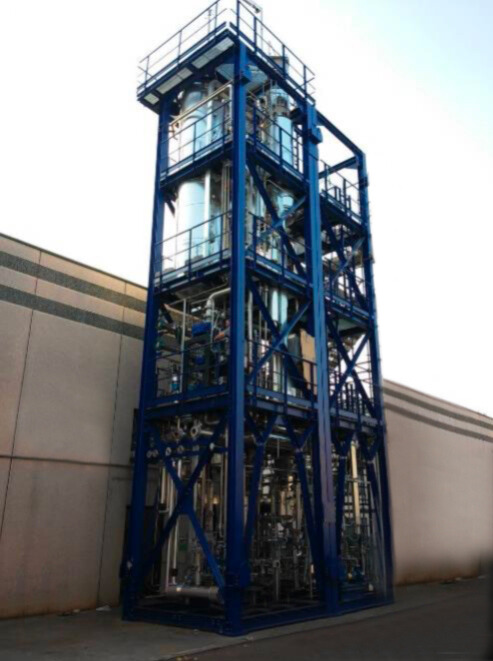
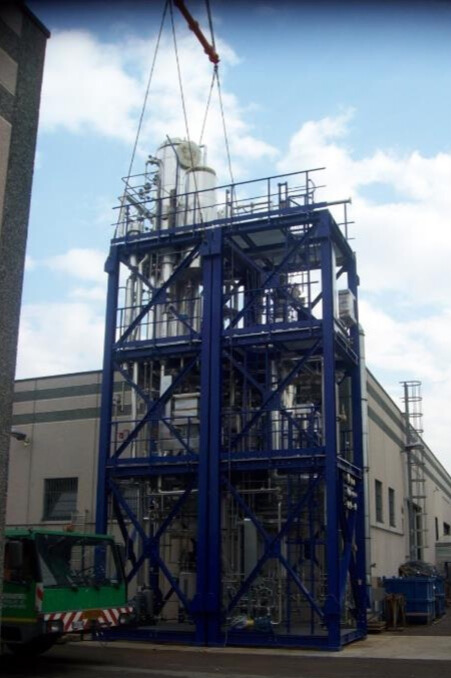
Plants
Oleochemicals purification
Oleochemicals include a broad range of products (fatty acids, fatty alcohols and others) produced starting from vegetable (e.g., olive oil, sunflower oil, citrus oil, hemp seed oil) and animal oils (e.g., fish oil), fats or even from unicellular microalgae (alternative source of polyunsaturated fatty acids – PUFA).
The processing of these products involves several stages and purification is essential to achieve the desired final quality, whether it involves pre-treated oils or fats or the derived products.
Purification may occur in several steps, according to the specific base material and the result to be achieved:
- removal of residual humidity, dissolved gases and other volatile compounds present in the edible oil and fat;
- removal of free fatty acids and thus reduction of edible oil or fat acidity;
- deodorization;
- removal of pesticides and pollutants;
- fractionation and concentration of fatty acids, fatty alcohols, fatty esters.
Thermal separation technologies such as evaporation, distillation and stripping, whether combined or not, are generally applied to obtain these results.
Overview
Show more Show lessOur purification plants for edible oils and fats usually include the following main steps and unit operations:
- De-gassing to remove the slightest impurities.
This is achieved through feed preheating and flash evaporation. - Removal of free fatty acids, odours or other pollutants.
The key unit operation is a short path evaporator (SPE). - Product cooling to avoid undesired degradation after the evaporation step.
Special heat exchangers are provided to quickly cool the product, and to improve thermal efficiency of the process.
In the case of purifying fatty acids, the plant’s operations may consist of:
- Separation of the heaviest acids (e.g., chain length above C18) from the lightest ones.
The key operation unit is generally a thin film evaporator. - Fractionation by evaporation and distillation of different fatty acids (e.g., C18, C20, C22).
The key unit operation is a thin film evaporator and a high vacuum distillation column. - Product cooling to avoid undesired degradation after the evaporation step.
Special heat exchangers are provided to quickly cool the product and to improve the process’ thermal efficiency.
Automatic or semi-automatic cleaning-in-place (CIP) systems can also be part of the plants to properly clean all the process parts. This step prevents cross contamination and facilitates the proper segregation of production batches.
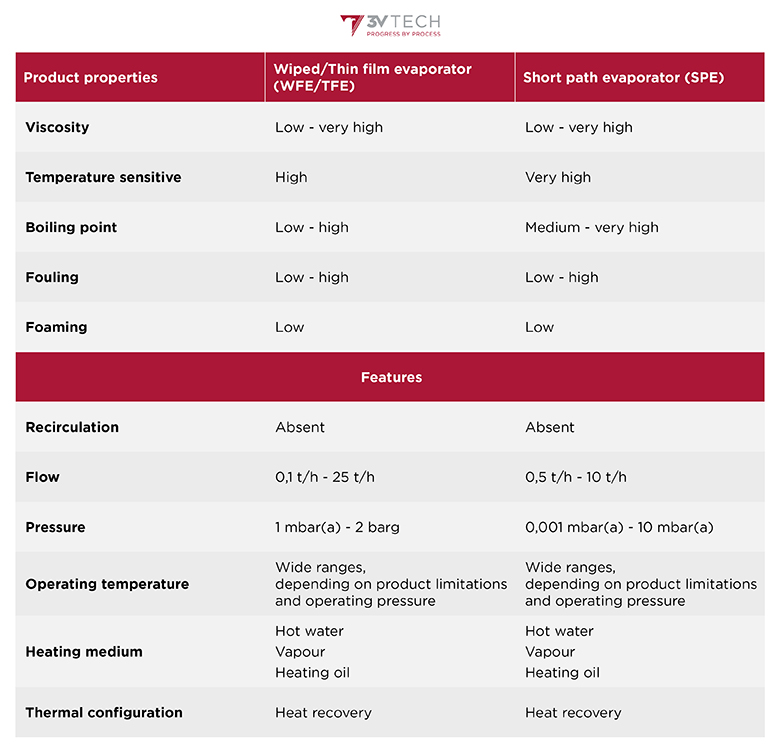
The special features of a wiped film evaporator (WFE) or a thin film evaporator (TFE) and, even more, those of a short path evaporator (SPE), facilitate delicate purification thus avoiding product thermal degradation and keeping all its organoleptic characteristics intact.
Multiple passes inside the same evaporator unit can improve separation efficiency while simultaneously reducing the initial investment.
For large production capacities, more evaporators can be combined in a series.
Energy consumption may be optimised by:
- Using hot water from cogeneration
- Using waste energy (e.g., exhaust gas, steam condensate and process condensate)
- Combining the abovementioned technologies
Features and rangeability
Show more Show lessPurification plants are customised according to the customer’s needs and expectations. Typical size features are reported below.
- Various rotor design, as lobed rigid rotor and bladed rotors are supplied.
- Available also as skid mounted units to minimise installation operations at the customer’s site.
The most suitable material is selected depending on the nature of the product and the operating conditions.
The main materials usually selected are the following:
- Stainless steels
- Super duplex stainless steels
- Nickel alloys (e.g., Hastelloy® HC22, Inconel® 600)
A wide range of services from technical feasibility studies to revamping existing plants is also feasible.
Key benefits
Show more Show less- High product purity
- No product degradation
- Versatility
- Customised design
- Bespoke thermal configuration
- Maximum energy savings
- High automation level
- Remote assistance
- Easy to clean
Specific benefits – wiped film evaporators or thin film evaporators
- Optimised heat transfer surface, thanks to the high heat transfer coefficient and the possibility to operate with a wide difference in temperature (∆T).
- High evaporation rate and short residence time with strong reduction of product degradation issues.
- No fouling problems thanks to the low residence time, high turbulence and continuous cleaning of the heated surface.
Specific benefits – short path evaporators
- High product purity thanks to the possibility to devolatilize also very high boiling impurities.
- No product degradation thanks to very low operating pressure, low evaporation temperature and short residence time.
Applications
Show more Show lessThermal separation technologies can be successfully used to purify a multitude of products, such as:
- Edible oils and fats (olive oil, sunflower oil, citrus oil, hemp seed oil, soybean oil, palm oil, cashew nut oil, rapeseed oil and fish oil)
- Fatty acid esters, including Omega-3 and Omega-6
- Glycerides (monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides)
- Biodiesel (methyl and ethyl esters – FAME, FAEE)
- Glycerine
More about our glycerine recovery plants
More about production processes
Depending on the nature of the product and the target sought, the purification process needs to be carefully identified through thermodynamic calculation, simulation and testing operations, all of which are conducted at our R&D centre leveraging our multidisciplinary teams.
References